library(psptools)
library(pspdata)
library(dplyr)
library(ggplot2)Class Imbalance
Class imbalance in training data using binary and multiclass bins
psp <- read_psp_data(model_ready=TRUE) Binary
Predicting probability of toxicity above/below closure limit
cfg <- list(
configuration="test",
image_list = list(tox_levels = c(0,80),
forecast_steps = 1,
n_steps = 2,
minimum_gap = 4,
maximum_gap = 10,
multisample_weeks="last",
toxins = c("gtx4", "gtx1", "dcgtx3", "gtx5", "dcgtx2", "gtx3",
"gtx2", "neo", "dcstx", "stx", "c1", "c2")),
model = list(balance_val_set=FALSE,
downsample=FALSE,
use_class_weights=FALSE,
dropout1 = 0.3,
dropout2 = 0.3,
batch_size = 32,
units1 = 32,
units2 = 32,
epochs = 128,
validation_split = 0.2,
shuffle = TRUE,
num_classes = 4,
optimizer="adam",
loss_function="categorical_crossentropy",
model_metrics=c("categorical_accuracy")),
train_test = list(split_by="year_region_species",
train = list(
year = c("2014", "2015", "2016", "2017", "2018", "2019", "2020", "2021", "2022", "2023", "2024"),
region = c("maine"),
species = c("mytilus")),
test = list(
year = c("2014"),
region= c("maine"),
species = c("mya")))
)binary <- transform_data(cfg, psp)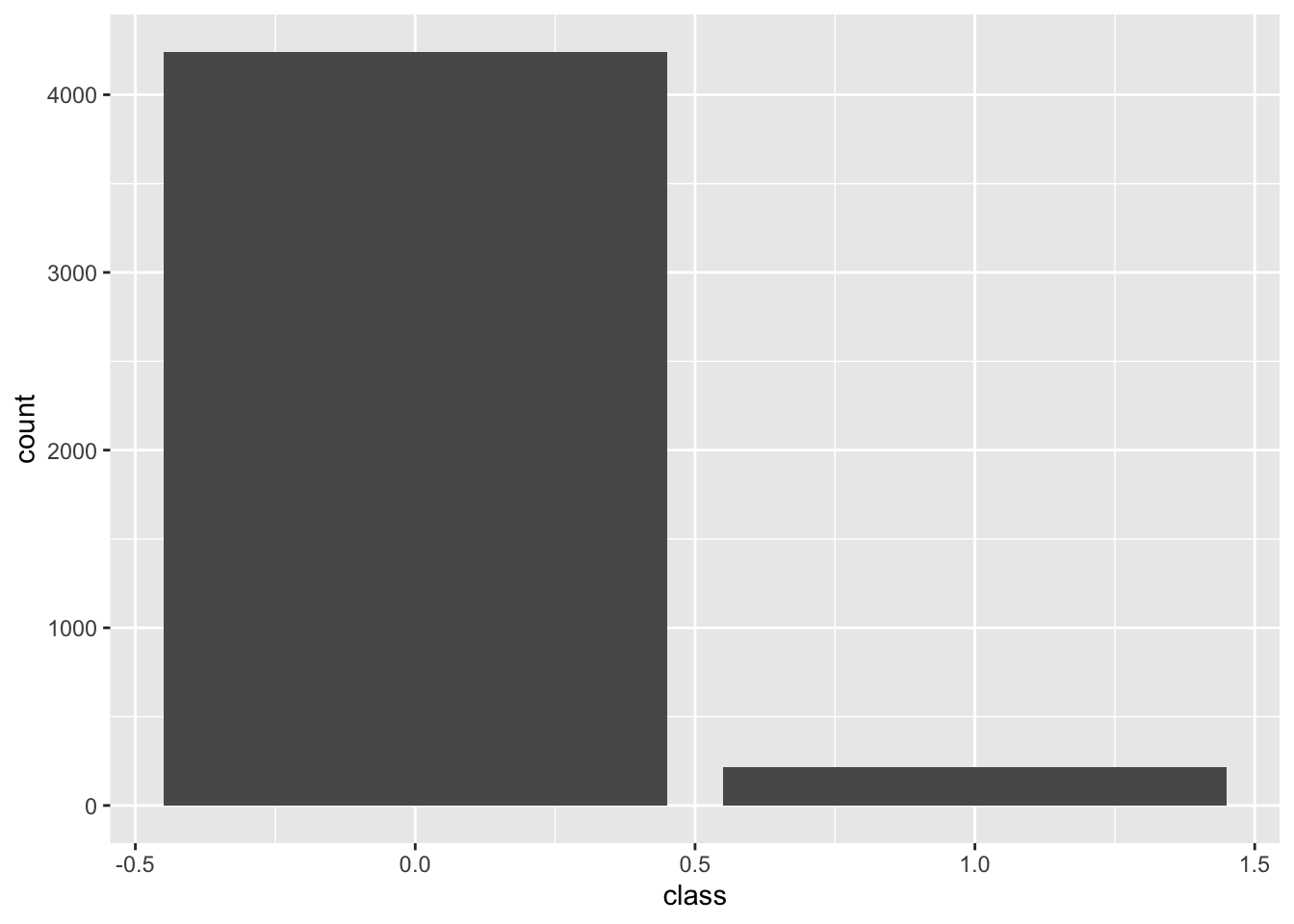
Multiclass
Predicting one of more than two toxicity classifications. Here we use 0, 10, 30, and 80 as cutoffs.
cfg <- list(
configuration="test",
image_list = list(tox_levels = c(0,10,30,80),
forecast_steps = 1,
n_steps = 2,
minimum_gap = 4,
maximum_gap = 10,
multisample_weeks="last",
toxins = c("gtx4", "gtx1", "dcgtx3", "gtx5", "dcgtx2", "gtx3",
"gtx2", "neo", "dcstx", "stx", "c1", "c2")),
model = list(balance_val_set=FALSE,
downsample=FALSE,
use_class_weights=FALSE,
dropout1 = 0.3,
dropout2 = 0.3,
batch_size = 32,
units1 = 32,
units2 = 32,
epochs = 128,
validation_split = 0.2,
shuffle = TRUE,
num_classes = 4,
optimizer="adam",
loss_function="categorical_crossentropy",
model_metrics=c("categorical_accuracy")),
train_test = list(split_by="year_region_species",
train = list(
year = c("2014", "2015", "2016", "2017", "2018", "2019", "2020", "2021", "2022", "2023", "2024"),
region = c("maine"),
species = c("mytilus")),
test = list(
year = c("2014"),
region= c("maine"),
species = c("mya")))
)multiclass <- transform_data(cfg, psp)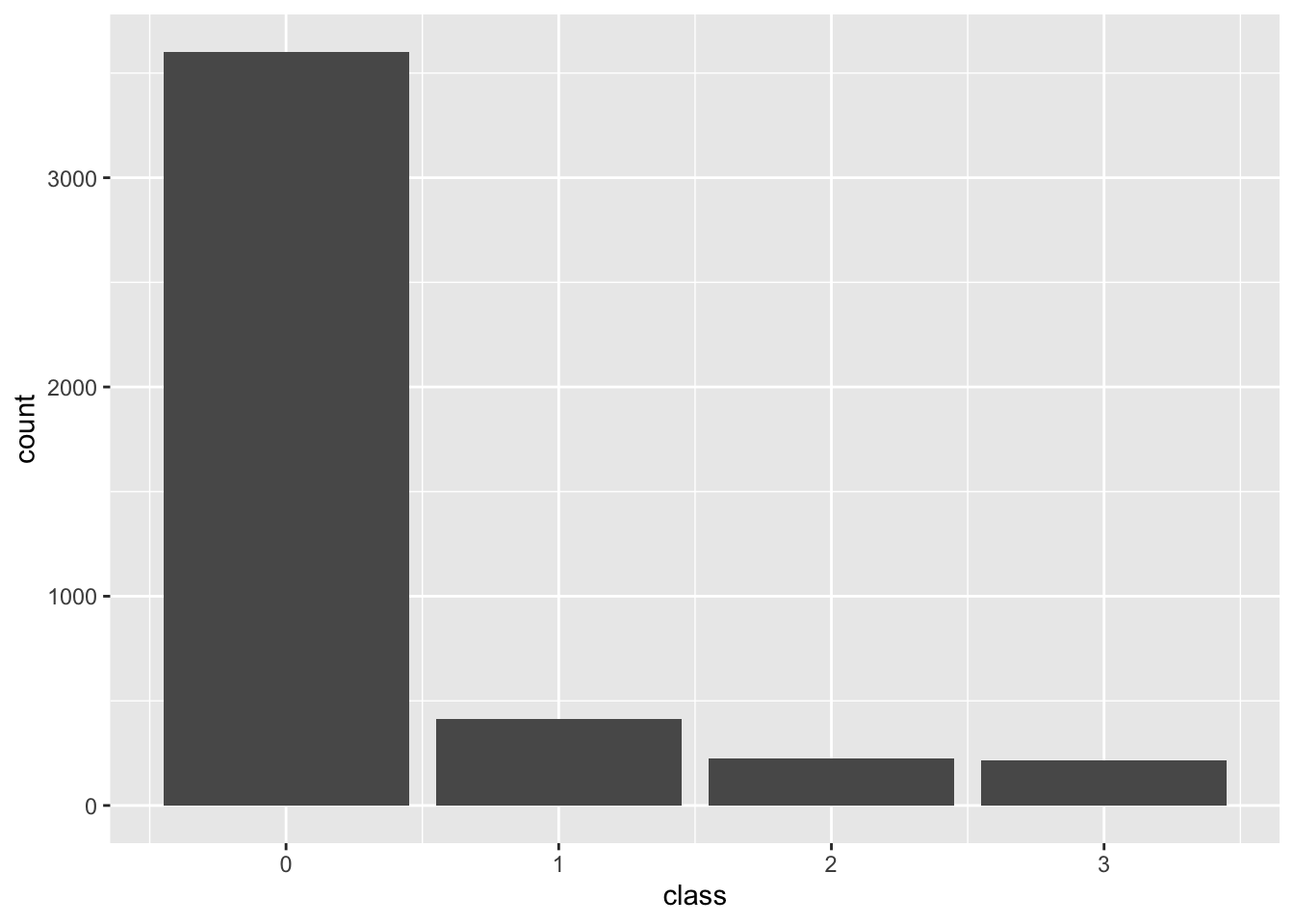
Classification counts in training data through end of 2024
# A tibble: 4 × 3
class n proportion
<dbl> <int> <dbl>
1 0 6775 0.782
2 1 972 0.112
3 2 511 0.059
4 3 410 0.047Techniques for overcoming class imbalance
Downsampling
The distribution of the classes becomes even. Since we only have around 200 samples in class 3 (the most rare), we will sample that many from each of the others.
cfg <- list(
configuration="test",
image_list = list(tox_levels = c(0,10,30,80),
forecast_steps = 1,
n_steps = 3,
minimum_gap = 4,
maximum_gap = 10,
multisample_weeks="last",
toxins = c("gtx4", "gtx1", "dcgtx3", "gtx5", "dcgtx2", "gtx3",
"gtx2", "neo", "dcstx", "stx", "c1", "c2")),
model = list(balance_val_set=FALSE,
downsample=TRUE,
use_class_weights=FALSE,
dropout1 = 0.3,
dropout2 = 0.3,
batch_size = 32,
units1 = 32,
units2 = 32,
epochs = 128,
validation_split = 0.2,
shuffle = TRUE,
num_classes = 4,
optimizer="adam",
loss_function="categorical_crossentropy",
model_metrics=c("categorical_accuracy")),
train_test = list(split_by="year_region_species",
train = list(
year = c("2015", "2016", "2017", "2018", "2019", "2020", "2021"),
region = c("maine"),
species = c("mytilus")),
test = list(
year = c("2014"),
region= c("maine"),
species = c("mytilus")))
)downsampled <- transform_data(cfg, psp)tibble(location = downsampled$train$locations, class = downsampled$train$classifications) |>
ggplot(aes(x=class)) +
geom_bar()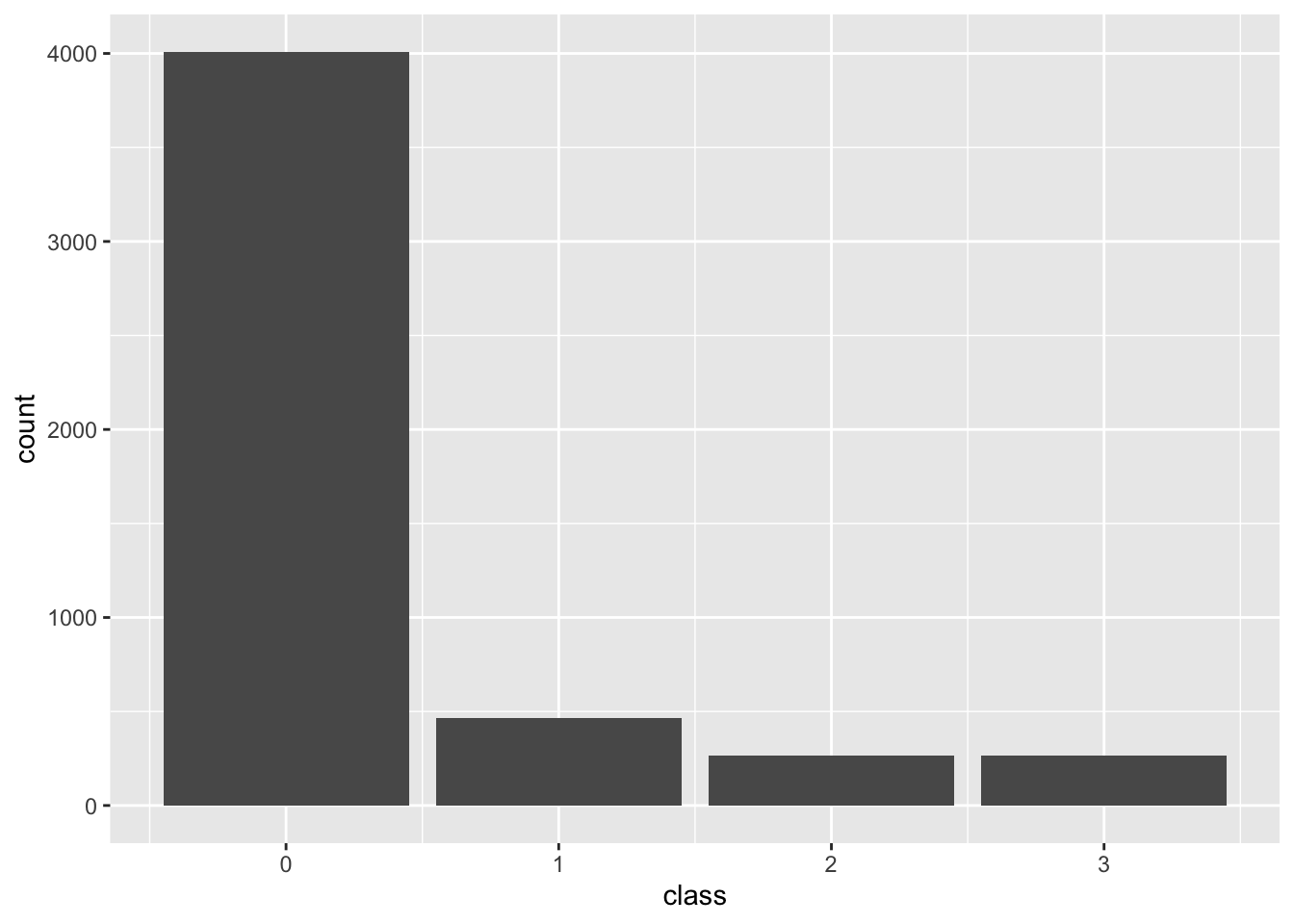
Validation set balancing
The keras::fit() function will let us manually assign the samples in the validation set, rather than choosing a random percentage with the validation_split argument. We can sample an even distribution of each class. Balancing the validation set can be combined with downsampling in the training set.
cfg <- list(
configuration="test",
image_list = list(tox_levels = c(0,10,30,80),
forecast_steps = 1,
n_steps = 3,
minimum_gap = 4,
maximum_gap = 10,
multisample_weeks="last",
toxins = c("gtx4", "gtx1", "dcgtx3", "gtx5", "dcgtx2", "gtx3",
"gtx2", "neo", "dcstx", "stx", "c1", "c2")),
model = list(balance_val_set=TRUE,
downsample=FALSE,
use_class_weights=FALSE,
dropout1 = 0.3,
dropout2 = 0.3,
batch_size = 32,
units1 = 32,
units2 = 32,
epochs = 128,
validation_split = 0.2,
shuffle = TRUE,
num_classes = 4,
optimizer="adam",
loss_function="categorical_crossentropy",
model_metrics=c("categorical_accuracy")),
train_test = list(split_by="year",
train = c("2015", "2016", "2017", "2018", "2019", "2020", "2021"),
test = c("2014"))
)#balanced_val <- transform_data(cfg, psp)#str(balanced_val)#tibble(location = balanced_val$val$locations, class = balanced_val$val$classifications) |>
# ggplot(aes(x=class)) +
# geom_bar()Weighted classes
keras::fit() also accepts a class_weights argument. psptools provides a function get_class_weights() to obtain these.
cfg <- list(
configuration="test",
image_list = list(tox_levels = c(0,10,30,80),
forecast_steps = 1,
n_steps = 3,
minimum_gap = 4,
maximum_gap = 10,
multisample_weeks="last",
toxins = c("gtx4", "gtx1", "dcgtx3", "gtx5", "dcgtx2", "gtx3",
"gtx2", "neo", "dcstx", "stx", "c1", "c2")),
model = list(balance_val_set=FALSE,
downsample=FALSE,
use_class_weights=TRUE,
dropout1 = 0.3,
dropout2 = 0.3,
batch_size = 32,
units1 = 32,
units2 = 32,
epochs = 128,
validation_split = 0.2,
shuffle = TRUE,
num_classes = 4,
optimizer="adam",
loss_function="categorical_crossentropy",
model_metrics=c("categorical_accuracy")),
train_test = list(split_by="year_region_species",
train = list(
year = c("2015", "2016", "2017", "2018", "2019", "2020", "2021"),
region = c("maine"),
species = c("mytilus")),
test = list(
year = c("2014"),
region= c("maine"),
species = c("mytilus")))
)model_input <- transform_data(cfg, psp)class_weights <- get_class_weights(model_input$train$classifications)
class_weights$`0`
[1] 1
$`1`
[1] 8.603004
$`2`
[1] 15.01498
$`3`
[1] 15.18561